
In today’s digital currency landscape, the significance of robust security and risk management systems cannot be overstated. These systems work hand-in-hand to ensure each transaction’s legitimacy and safety. However, in pursuit of convenience, some users bypass these critical protections by opting for “blind signing”. While this approach may seem to streamline the process, it introduces substantial risks.
Understanding Blind Signing
Blind signing occurs when users sign data without running it through security checks and risk management systems. Although it appears to simplify transactions, it opens the door to severe vulnerabilities. It’s akin to leaving your house unlocked—you never know what issues might arise.
The Risks of Blind Signing
Skipping security and risk controls when blind signing introduces significant threats:
Exposure to Interception and Tampering: Without protective measures, signed messages are vulnerable to interception and alteration, such as in man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. During transmission, an attacker can hijack and modify signature data, ultimately gaining control over the user’s transactions. Our security system mitigates this risk with end-to-end encryption and multi-layer verification. For instance, in 2022, BAYC holders fell victim to a phishing attack that exploited blind signing. Users unknowingly signed transactions that transferred valuable NFTs instead of verifying ownership. Lacking proper risk controls, they suffered millions in losses.
Executing Incorrect Transactions: Even if an attack is avoided, blind signing still risks user error. Complex transaction structures can lead to costly mistakes, such as transferring 10 million units instead of 100. With systems like Cactus Custody’s, risk controls catch such anomalies. For example, a withdrawal limit can block attempts that exceed set thresholds, while address whitelists prevent transactions to unauthorised addresses.
Preventive Measures
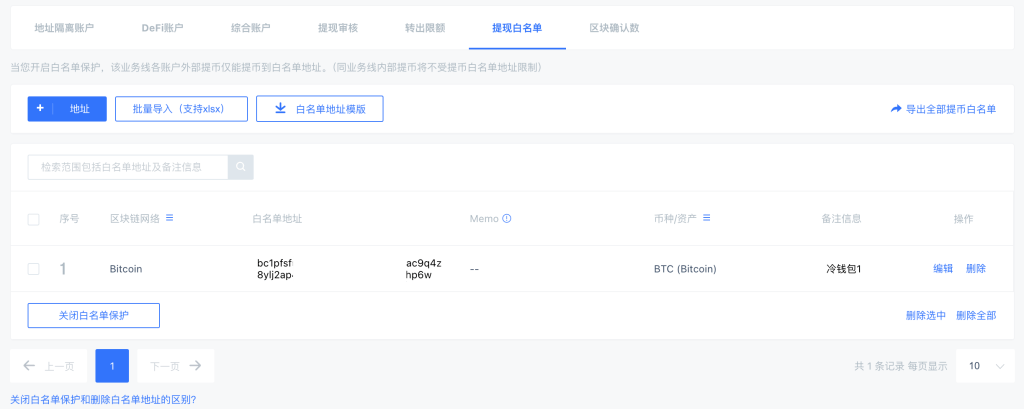
Enable Address Whitelisting: Activating an address whitelist is a crucial defence against blind signing risks. By pre-approving trusted addresses, transactions outside the list are automatically blocked. This feature minimises the chance of funds being misdirected due to user error or malicious intent. Even if a phishing attempt is made, non-whitelisted transactions are stopped.
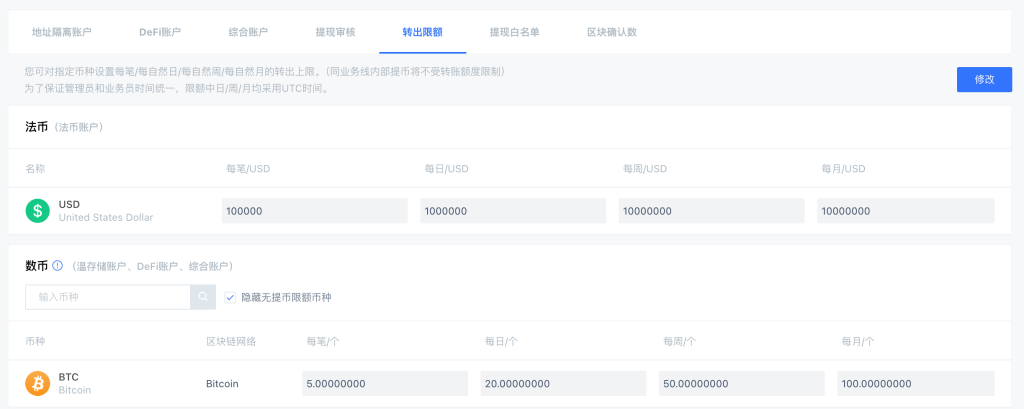
Set Withdrawal Limits: Limiting withdrawal amounts is another crucial safeguard. Users can reduce the impact of errors or theft by capping individual transactions or daily totals. Setting limits based on risk tolerance ensures that large transfers are blocked or trigger additional verification. This buffer gives users time to react and mitigate potential losses.
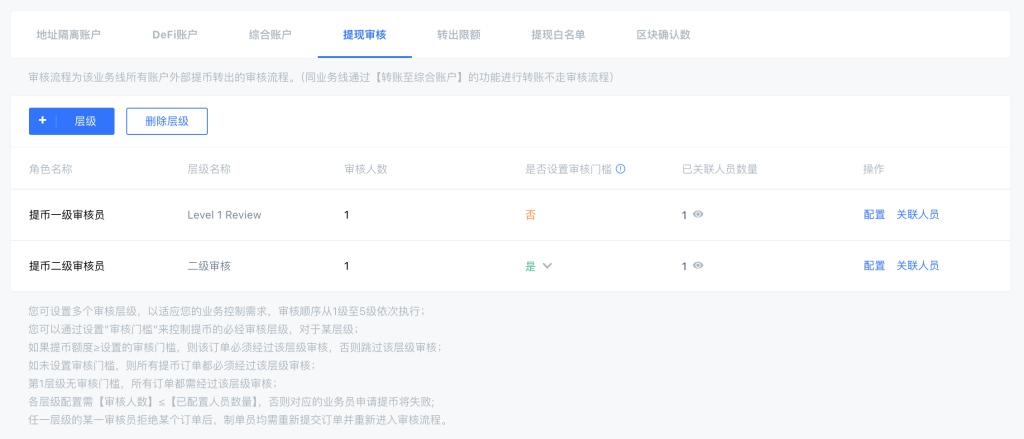
Implement Multi-Layered Approval Processes: A hierarchical approval system should be in place for added security. Delegating transaction reviews across multiple roles ensures no single point of failure. For example, while a user may initiate a large transfer, final approval and signature require supervisory and risk control team validation. This multi-step process identifies issues early, preventing costly mistakes.
The Critical Role of Security and Risk Control Systems
Security and risk control systems are the backbone of secure digital currency transactions. Our solution employs multi-layered defences to block unauthorised activities while continuously monitoring and analysing transactions for potential risks. These systems act as your protective armour, allowing you to engage in digital finance with confidence and peace of mind.
Conclusion
In the dynamic digital currency world, convenience is valuable, but security should always come first. While blind signing may seem efficient, the risks far outweigh the benefits. Relying on solid security and risk control systems is a more thoughtful, safer approach than compromising security for temporary ease.